Reproducibility in life science research
M Hallett
21/07/2020
Tools to facilitate reproducibility
Where things can go wrong
Solutions and mitigators
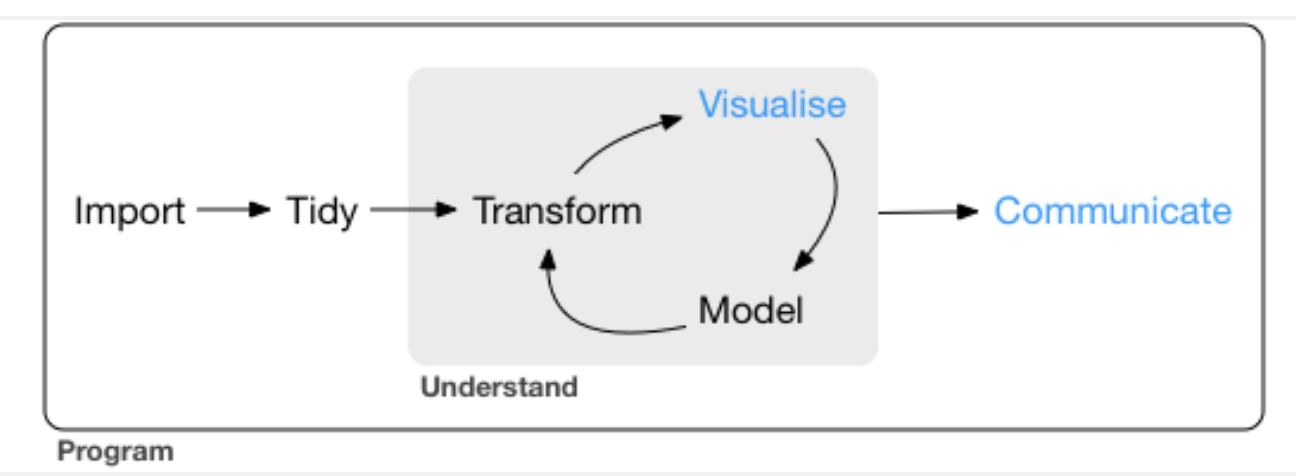
Towards Systems Biology

- Systems Commerce, Information Systems, Systems Biology: what advantages does good design have?
Reproducibility crisis
Reproducibility crisis. The wiki page gives a decent overview to the problem and surveys the major angles for addressing this issue.
The fundamental observation is that many studies in the literature are not reproducible by third parties.
Some disagreement as to the severity of the problem or how to deal with the problem.
What can we do as quantitative life sciencists (data scientists, bioinformaticians, computational biologists)?
Complete dishonesty
There are examples of clear dishonesty in life science research.
However issues of reproducibility (or lack thereof) are more insidious.
The causes of irreproducibility
Simple clerical mistakes
Poor or incomplete description of the result
Poor or incomplete description of method
Problems (eg technical or selection bias) in profiling
Inaccessible supporting data incl. training set
Improper use of training/validation dataset
Bugs in computer code
Lack of statistical power in the study
Improper or naive use of statistics (eg pvalues) Why most published research findings are false, Ioannidis
Society and human nature: competition, time constraints, poverty, acknowledegment
Other?
How can the quantitative life sciences contribute?
Bioinformatics’ mandatesinclude development of ethical guidelines, standards and education.
Data science contributes methods for better expressing our results.
Computational biology continues to improve methodology and integration with solid statistical foundations.
Incomplete information in manuscript
For example,
Problem Poor or incomplete description of the result
Problem Poor or incomplete description of method
Mitigation Distill A new way of publishing?
Mitigation Distill for R
Poor description of methodology; lack of code
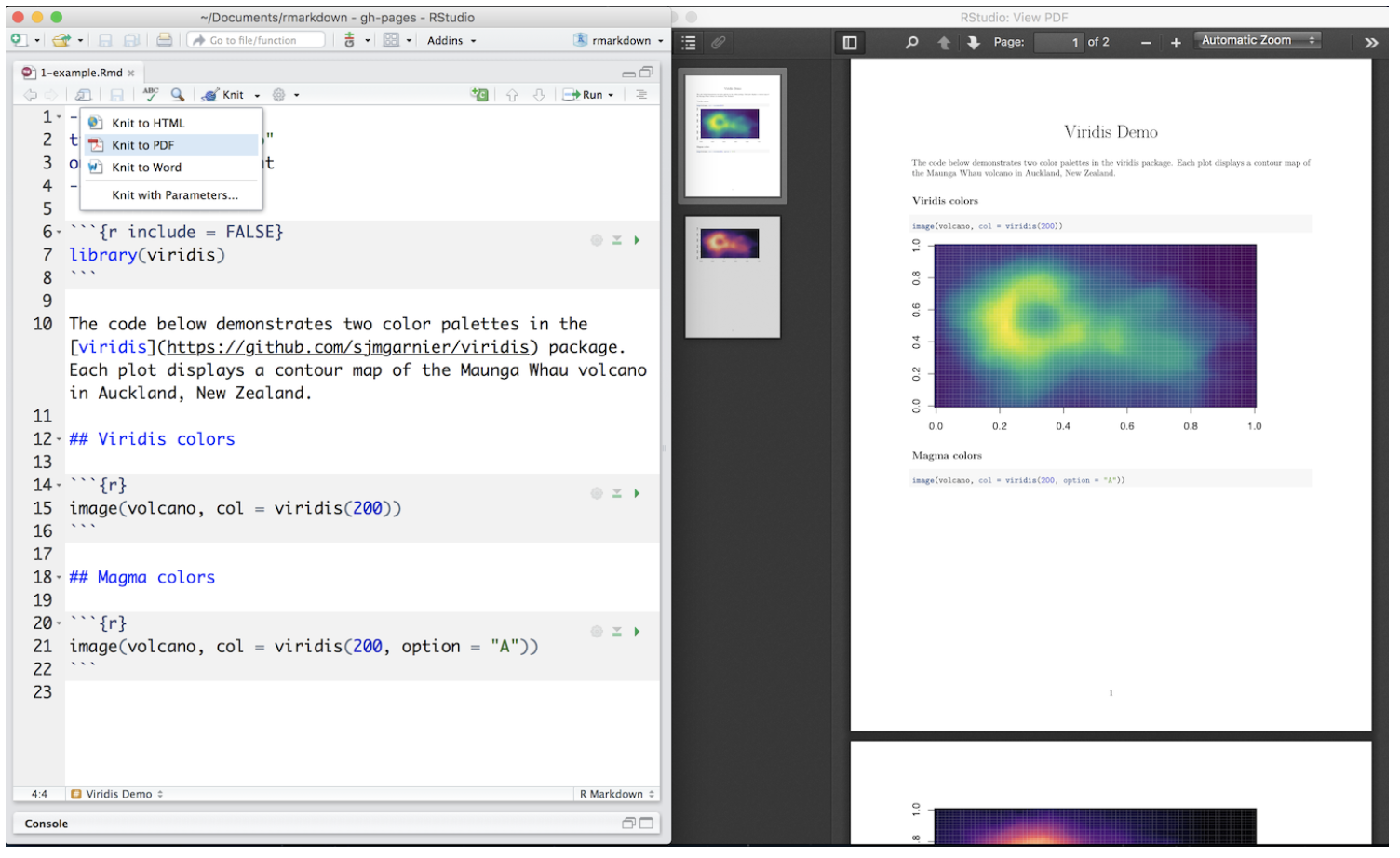
GIT
- GIT is software that guarantees persistent and consistent code wtihin collaborative projects.

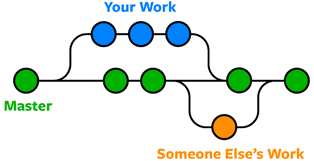
Bitbucket, Github and other sites
- There are websites that specialize in hosting GIT repositories. This makes your projects accessible everywhere.
Github, Bitbucket and other sites
Acknowledgement
- Outdated method of listing authors
BIOL 480
© M Hallett, 2020 Concordia University
